Yaws is a poverty-related, infectious skin disease that affects mainly children below 15 years of age (with a peak between 6 and 10 years) in warm, rural, tropical areas in Africa, the Western Pacific Islands and Southeast Asia. About 75% of people affected by Yaws are children. It occurs in overcrowded communities, with limited access to basic amenities such as water and sanitation, and limited health care. It is said that “Yaws begins where the road ends”.
 Yaws mainly affects the skin but can also involve the bone and cartilage. Early detection and treatment can avoid gross disfigurement and disability which occur in about 10% of cases.
Yaws mainly affects the skin but can also involve the bone and cartilage. Early detection and treatment can avoid gross disfigurement and disability which occur in about 10% of cases.
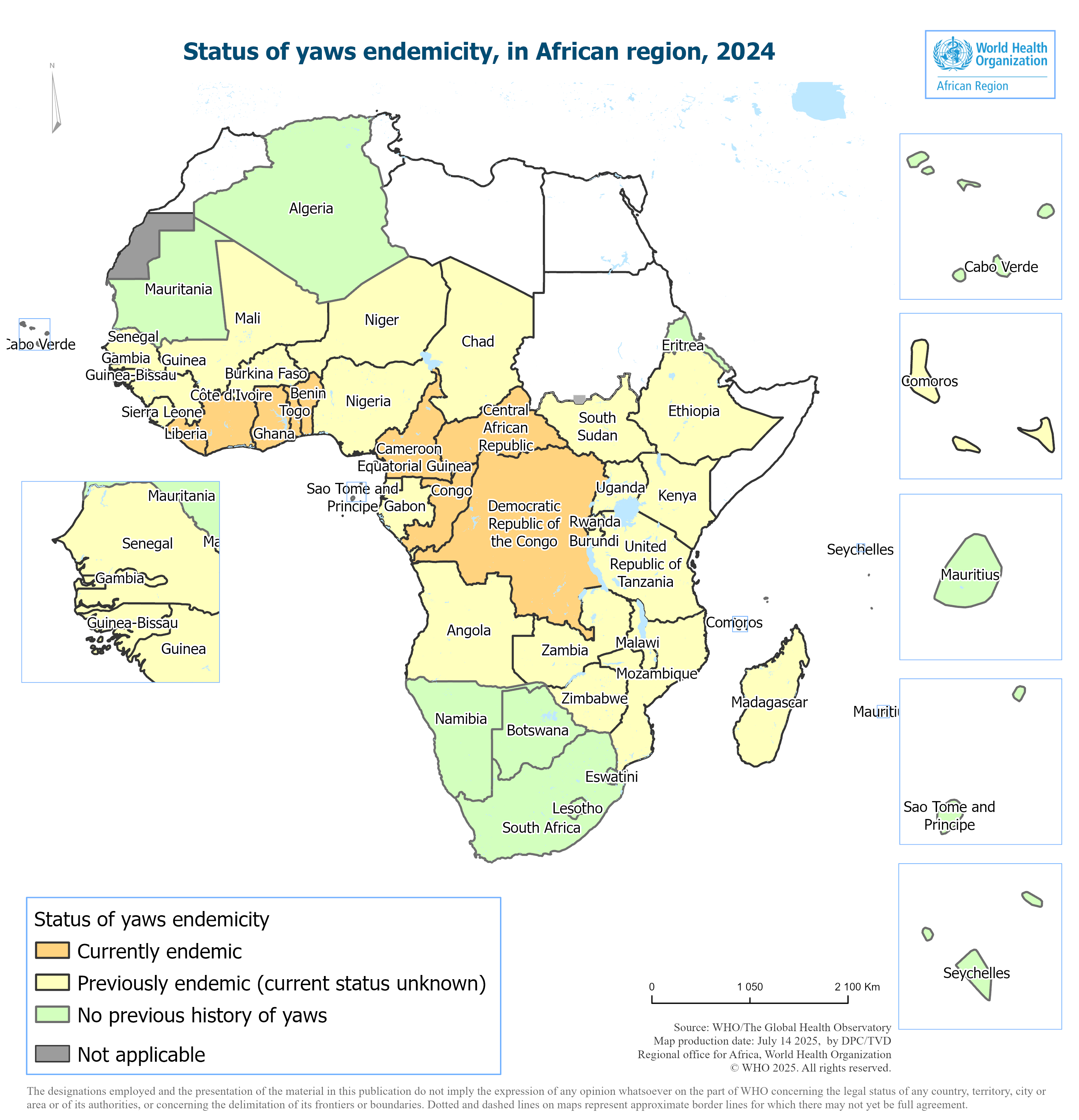
As of 2024, Yaws is currently endemic in 16 countries worldwide, while 82 countries, areas and territories are considered previously endemic.
The Yaws epidemiologic situation in 2024 in the Africa region is as follows:
- 9 countries currently endemic (Group A): Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Côte d’Ivoire, Ghana, Liberia, Congo, Democratic Rep. Congo, Togo
- 26 countries previously endemic current status unknown (Group B)
- 12 countries no previous history (Group C): Algeria, Botswana, Cabo Verde, Eritrea, Lesotho, Mauritania, Mauritius, Namibia, Sao Tome and Principe, Eswatini, Seychelles, South Africa.


